Diploma Theory imp questions
Diploma Important questions Paper 1
1Q.Explain different aspects of improvised music?
ans.The rendering of Carnatic music id of two types:
1)Kalpitha Sangeetham: The compositions are already composed, practiced, memorized, and performed
1)Kalpitha Sangeetham: The compositions are already composed, practiced, memorized, and performed
2)Kalpana Sangeetham: Performed extemporized on the spot
Kalpana Sangeetham or Manodharma sangeetham is one of the important aspects of Indian Music.
It is the most essential aspect of Gana Sabha. It occupies the third part of the concert time.
The performer has to keep in mind the RagaLakshana, Jeeva Swaras, Nyasa Swaras, and special Prayogas while performing so as to bring the essence of the raga.
The manodharmam has 5 main aspects:
1)Ragam
2)Thanam
3)Pallavi
4)Nearaval
5)Swarakalpana
Ragam:
RagaAlapana:
Ragalapana consists of 3 main stages:
Akshipthika:
Akshipthika:
- This is the introductory part of the RagaAlapana.
- Usually starts with mandthraSthayai Sadhjamam
- It is here the manifestation of the RagaAlapana starts
- The sancharas include mostly of mandhrasthayi and sometimes also have tharasthayi sanchars.
- Sometimes the the akshipthika may also start with Thara Sthayi based on the tradition.
- This is one of the substantial parts of ragaAlapana.
- This in turn has 4 stages:It has a commencement or edupu and ends with mukthayi or vidhari.
- Thus the vidhari act as the crowning part of the ragam
- Prathama Raga Vardhini:
It is mostly in slow tempo - starting with madhyastahyi sadjamam and goes to mandhrasthayi shadjamam. Sometimes even Madhya stayi sancharas also occur.
- Vishesha Prayogas and ragas which portray the identity of the raga are introduced.
- This part of the ragam should be able to let the rasika identify the ragam and singer should throw light on the ragam properly.
- Dwitheeya Raga Vardhini:
- Medium tempo
- mostly madhya stahyi occasional flights to other sthayi
- One can go up to Tarasthayi Madhyam and Tarastahyi Stahyi Madhyama
- Return to Shadjamam sancharas
- Thritheey Raga Vardhini:
- Usually medium tempo to fast tempo
- mostly in madhya stayi
- sometimes rarely touches thara sthayi
- Chathuartha Raga Vardhini:
- This is where the singer delineates the ragam.
- Mostly faster tempo
- singer using the gandaram rishabham and shadjamam in thara sthayi.
- Also covers the middle octave
- Tries to cover all the raga ranjaka prayogas
- Sthayi and Makarini:
*This part is usually fast - Starts with a same note and ends with note which is very near to the starting note or sometimes may end on the same note as it started.
- It is called brigas or longer range faster singing
- When the performer starts singing this the audience know that the ragam is about to conclude.
- It is a balance of thalam and ragam
- We do not have a particular thalam or avarthas but just follow a single beat to maintain the rhythm.
- Thanam is madhyakalaghanam.
- The phrases ananta,tanamta,tananna,tanamna should be used in thus style of raga exposition.
- Experts play trikala thanams.
- Eight varieties of thanam have been recognised,
- The rhythmic flow of music is very fascinating
- they are:
- Manava
- Asva-Horse
- Gaja-Elephant
- mayura-peacock
- chakra-circle
- manduka-frog
- Markata -Monkey
- kukuta-Cock
- Pallavi is the most important concept of manodharma
- It puts to test the mastery of rhythm, technical skills, and creativity.
- The Pallavi must cover the the aesthetics of the ragam and should provide intellectual joy and joy.
- The word pallavi is divided into three words:
- Pa="Padhagarbham"
- la="Laya"
- vi="Vinyasa"
- The Pallavi can be made in any language
- A meaningful sentence with two parts is taken for Pallavi
- Prathamaanga and Dvityanaga are two parts of a Pallavi and the dividing point is called arudhi or padagarbham.
- The arudhi is usually like a resting point and in Aadhi thalam it usually occurs on the first dhrutham
- meaning filling up
- it means we have to fill up the Pallavi with new sangathis
- You need to keep in mind the rhythm and the phrases of the Pallavi
- The position of the phrases should be the same as in the original Pallavi.
- Neraval starts with madhyama kalam and ends at Paikalam.
- Gradually the sangathis end up taking a new form
- and finally, the singer comes back to the original sangathi
- This is continued with Swara Kalpana
Swarakalpana:
- It is a sequence of swaras that represent the raga bhava
- The swaras are rendered with proper intonation,gamkas,sruthis
- Some special sancharas are kept in mind
- While doing the Swara Kalpana the performer has to keep in mind the thalam and which note he/she to end with so as to reach the Sahitya
- the Swara Kalpana can be done on Pallavi, anupallvi or charanam
- The place where Swara Kalpana is done is chosen such that the Sahitya is appropriate, enjoyable, and has a deeper meaning.
- Musicians while doing Swara Kalpana should keep in mind the following points :
- Swaras of particular raga
- in first speed and second speed
- in one avartha
- two avarthas
- murchana
- Anya Swara
- Raga bhava
- Gati bhedha
- Mridanga jathi
- Muktahyi calculations etc.,
- Musicians should practice the different permutations and combinations, Janta and dhatu swaras to gain command over the Swara Kalpana pattern.
- Swati Tirunal (1813- 1846), the Royal composer of Travancore
- It is to Harikesanallur Muthiah Bhagavathar and Semmangudi Srinivasa Iyer that we owe the popularity of Swati Tirunal’s compositions.
- Some of the famous ones are Deva deva (Mayamalavagowla), Mamava sada janani (Kanada), Mamava sada varade (Natakurinji), Pankajalochana (Kalyani), Sarasija nabha murare (Todi). Bhogeendra sayinam in Kuntalavarali is a lilting melody..
- His Ramayana kriti Bhavayami Raghuramam, originally in Saveri was retuned to a brilliant ragamalikai by Semmangudi.
- Subbaraya Sastry (1803-1861)
- the second son of Syama Sastry had the unique privilege of studying with each of the Trinity.
- His Reetigowla gem, Janani ninnu vina, is one the staples of the concert repertoire.
- Many of his kritis have beautiful swara sahityams, a la his father’s; good examples are Sankari nee yani (Begada), and Ema ninne (Mukhari).
- Again like those of his father, most of his compositions are in praise of goddess Ambal, However, the Hamir Kalyani kriti, Venkata saila vihara is on the deity of Tirupathi.
- Patnam Subramania Iyer (1845-1902) was among the most prominent composers of the late nineteenth century.
- He was a disciple of Manubuchavadi Venkatasubba Iyer, a cousin and a senior disciple of Thyagaraja.
- Both of them composed kritis and other pieces with the mudra of Venakatesa leading to a confusion as to which piece is whose.
- In particular the well known navaraga varnam, Valachi vachi is sometimes attributed to the latter.
- Patnam is famous for his tuneful kriti Raghuvamsa sudha in Kadana kuthuhalam, a top favorite with instrumentalists The brilliant chittaswara for this kriti is unforgettable.
- His renditions of Begada were supposed to have been so masterly that he was also called “Begada” Subramania iyer .
3QClassifiacation of instruments and explain any percussion instrument.
(I would suggest you to go through all the types ka one example each)
Ans.Classification of musical instruments:
- Percussion
- Drone
- Wind
- String
- Percusion:
- Mridhamgam
- Ghatam
- morsing
- Drone:
- Thanpura
- Wind:
- Flute
- String:
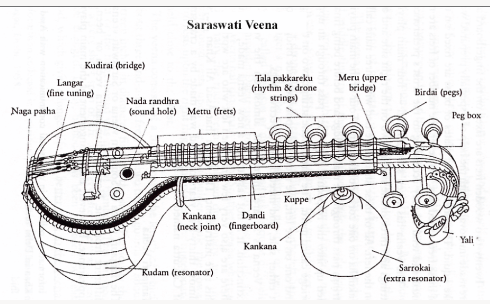
- Veena
- Violin
Learn drawings and description of each instrument
Each category at least one
4QExplain about different musical compositions and their types?
- Geetham:
- Geetham is a union of daathu and maathu.
- the union words of lyrics and swaras
- Geetham literally means song
- It is the first lyrical composition taught to a student
- Geethams were extensively written by Purandhara Dhasa,PydalaGurumurthy,Vekatamakhi
- In geetham you sing everything from beginning to end without repetions
- Geethams are written in all saptha thalas
- Geetham is of two types:
- Sanchari Geethas
- Lakshana Geethams
- Sanchari geethas are usually in the praise of God .
- Whereas, Lakshana Geethas describes the structure/lakshana of the ragam
- Types of Sanchari Geethams:
*Pillari geethams-sung on deity - Rakthi raga geethams:-ragams like mohana
- Ghana raga geetham:-ghana ragas me composed
- Raagamalika geetham:-different ragas
- (Write one example for each if you can remember)
- Also called jathi swaram
- has only swara part
- Usually they are set to madhyama kala
- Usually in Aadhi thalam or chapu thalam
- They have 3 parts:
- Pallavi
- Anupallavi
- charnam
- Some do not have 3 parts , the only contain pallavi and anupallavi.
- Rules for rendering :
- Sing Pallavi
- after pallavi charnam 1
- after charnam 1 go back to Pallavi and render the next charnam
- if anupallavi also exists, then sing anupallavi after Pallavi and continue as above mentioned
- Sometimes mridanga jathis also occur hence sometimes called jathi swarams
- they usually have 4-8 Charanams
- Some prominent composers of swarapallavi are:
Swathi thirunal - Vadivelu
- veena krishnamacahari
- swarapallavi examples if you can give any
- (I only know hindhola ;)
- Taught after swarapllavi
- has both swaram and Sahitya
- consists of Pallavi,Anupallavi,Charanam
- The Charanams usually start with all the swaram in the ragam in ascending order.
- One of the famous Swarajathi is Bhairavi
- It portrays the entire raga bhava in it and it is beautifully composed.
- Swarajathis are more musical and higher importance is given given to melody instead of jathis
- Swarajathis are composed keeping in mind the bright colours of a raga
- examples:RaraVenu-aadhi-Bilhari
- Shambhashivaya-Adhi - khamas
- Kaamakshi - Misra chapu - Bhairavi-Syamasastri
- Some prominent composers :
- Swathi thirunal
- Syama sastri
They are like pillars for a student of music
They are a part of abhyasa ghanam
They consist of pallavi, Anupallavi,mukthayi and charanam and chittaswarams
They are usually rendered in two kalams
sometimes rendered in thrisram as well
it is the choice of the performer
(Write the procedure of rendering)
Varnams depict the entire ragabhava and different sancharas or prayogas that can occur in the particular raga
Varnams are stepping stones for Kruthis and swarakalpana as the chittaswarams help the student in understanding the creative part of music
Usually Varnams have four chittaswarams
- The first chittaswarams have lot of dheerga swaras and relatively slow
- The second has fewer dhergas and usually has patterns
- The third has either very less or no dheergas and this is a little faster paced
- The last one is a combination of dheergas and patterns it is a little fast-paced
Thana Varnam: has sahithya to only Pallavi anupallavi and charanam
Pada Varnam:All parts have sahityam usually used in dance.
Raagamalika Varnam: composed in more than one raga
Thillana:
The pallavi and anupallavi have different mridanga jathis
It is usually used for dance
It is a very rhythmic and powerful piece of composition
The Charanam has sahitya , which is in the praise of god.
The concluding part that is the Charanam Anubandha has jathis and swarams alternatively
Some famous composers are Swathi Thirunal, Balamuralikrishnan,Lalgudi Jayaraman
It is usually sung at the end of the concert
Examples of Thillanas you know:
Mand
Kunthalavarali
Pharaju
Desh
*kind of musical composition
*more importance is given to sahitya and bhavam using music
*It was mostly composed by Purandara dasa in Kanada called Devarnamas
*In Telugu Annamarchya composed a lot on Sri Venkateshwara of Tirupathi
*some keerthanas have Swarasahithyas or jathis in between and called solukattu swaras.
*They are usually composed in easier and rakthi ragams and are usually composed in Aadhi Thalam
*Types:
- Ekadhatu-The pallavi and charanam are sung to same dhatu
- Example:
- Ramabhadra Rara aadhi thalam Shankarabharnam
- Dwidhatu-Pallavi and anuoallavi have same dhatu and cahranam has different dhatu
- Rama Dasharadha Rama-Annamacharya - visharadha
- Dhwithala
- Keerthana can be sung in different thalams
- Birana-Kalyani ShyamaShastri-Trisrajhathi can be sung not only in ekathalam but also in Chathrushra jathi rupaka thalam
- Bhakti
- Sringara
- Vasanthothsva: Composed during the spring festival for the god
- Sanksheeptha Ramayana: Thyagaraja Swamy composed them to briefly explain Ramayana
- Adhyatma Ramayana: Composed by Munipalle Subramanya Kavi. It has the entire Ramayanam from BalaKanda to Yudha Kanda.It starts with "Vinave Souricharithuni".
- Manasa Pujar
- Utsava Sampradaya: Keerthanas composed for special occasions called utsavams
- Divya Nama: Do not have anupallavi all charanam have the same dhatu
- Nindhasthuthi: Composed when devotee finds fault with God, but still rooted to his Bhakthi Marga way of convincing the god to listen to him.
Give some examples and famous composers you know
Kruthi:
- One of the most important musical composition
- It is usually taught alongide a varnam
- Kruthis are an epic of raga
- They are composed in such a way to give the essence of the raga
- They have different sangathis
- Kruthi has the following parts:
- Pallavi
- Anupallavi
- Charnam
- Charana anubandha
- Chitta Swaram(Not always)
- They are an important form of musical composition in a concert format
- Here more importance is given to melody and composed in different ragams and thalams it need be rakthi ragams only
- Kruthi is capable of having the navasrasas
- Thyagaraja had a very unique style of composing kruthis
- He would comppose in such a way that the ragabhava would be slowly elaborated
- The pallavi would expand it with a few sangathis , and the anupallavi slightly further and charnam would with more sangathis and gamakas elaborate the ragam.
- Some composers:
- Musical trnity
- Patnam Subramanyam Iyer
- Subbarayya Sastry
- (Give examples of your choice)
- If this is for 15 marks
- Method of singing the kruthi
- First Pallavi , Anupallavi , Charanam and chittaswaram (Explain them with repetions)
- Example of kruthis which have chitta swaras:
- RaghuVamsha-Kadhanakuthuhalam-Aadhi Thalam-Patnam Subramanyam Iyer
- RaghuNayaka-Hamsadhwani - Tyagaraja-Aadhithalam
- Paridhanamichithe-Khandhachapu-Patnam Subramanyam Iyer-Bilhari
- Examples of kruthis with Swara Sahithyas:
- Janani Ninnnuvina-Reethigowla-misrachapu-Subbaraya Sastry
- Marivere-Anandhabhairavi-misrachapu-Shyamasastry
Padams:
- The word padam means devotional song
- They are krithis in format
- They usually have Bhakthi and sringara rasa
- They are usually sung at the end of the concert
- They are of very slow tempo
- Most of them are in Vilamba Trisra triputa
- also some are in misra chapu thalam
- The padams are absolute musical forms,with sophisticated music in them
- They contain Pallavi anupallavi charnam and charna anubandha
- Some composers:
- Kshetrayya, Purandhara Dhasa,Swathi Thirunal,Ghanam Senayya
- Examples:
- They are in krithi format
- mostly sringara rasa
- composed in Rakthi ragas such as Pharaju Jhanjhuti behag Khamas
- Usually composed in Aadhi Thalam or Rupaka Thalam
- Music in Javalis are very lively and scintillating
- They have the following components:
- Pallavi
- Anupallavi
- Charanam
- Sometimes there are multiple Charanams
- Some composers are: Patnam Subramanyam Iyer,Ramnad Srinivas Iyengar,Dasu SriRamulu.
Apaduruku Khamas-aadhi Thalam
Ashtapadhi
- As the name suggests this has 8 lines
- It was composed mainly by Jayadheva in the 12th century who was a devotee of Krishna
- It depicts eternal love and devotion to the diety
- Each Astapadhi is in different Ragam and thalam.
- Gita Govindham of JayaDeva is a well-known Ashtapadhi
- It has twelve chapters divided into 24 Prabahandhas.
- The prabhandhas contain couplets grouped in eight called ashtapadhis
- JayaDeva composed this in Jaganatha temple in puri while his wife danced for it. It is called GithaGovindham as it is a song of Govinda
- His Ashtapadhis have the mudra "Sree Jayadeva Kavi"
- Two types :
- Dharshana Ashtapadhis
- Sanjeevani Ashtapadhis
- Each Ashtapadhi contains Pallavi Anupallavi and charanam
- Sometimes only charanam
- Some composers:
- Venkatamakhi-Thyagarajashtapadhi
- Sri Chandrashekara Shivas Ashtha padhi
- Rama Kavi - RamaAshtapdhi
- Example : Pashyathi Dishi Dhisi
- Sindhubhairavi-aadhithalam
Taragam:
- Extensively composed by Narayana teertha
- Narayana teertha is considered as the incarnation of Jayadevaof the 12th century who composed Githa Govindham
- Has 12 parts
- consists of
- Pallavi
- anupallavi
- charanam
- Anupallavi and charanam have the same dhatu
- It has Narayan Theertha as mudra
- It is preceded by a sloka and vakya
- The slokas are crisp musical dialogues
Krishnam Kalaya Sakhi-Mukhari - Aadhi
Jaya Jaya Swamin-Hamaswadhani-Aadhi Thalam
Daruvu:
- The music is ordinarily in madhyma kalam
- It is mostly seen in dance dramas
- The theme may be Sringara or historical
- The word Dharuvu can be traced to the ancient word Dhruva
- Types of Dharavu :
- Pravesha dharavu:
- It is the entrance song in dance drama
- Varnana Dharuvu:
- It is the descriptive Dharuvu
- Samvadha Dharu:
- Is a musical Dialogue
- Kolata Dharuvu:
- Used in stick play
- They have Pallavi,anupallavi, and charanam
- Some of them are composed in couplers or quartins
- Merattur Venkata Sastry has composed some beautiful Dharuvus in Telugu
Prabhandham
- Prabhandham is a type of musical composition and well known among linguistics
- Infact it is said that every composition is a form of prabhandham
- Venkatmakhi mentions in his "Chathurdhandi Prakasika" about Prabhandham
- During 5th century matangamuni mentions about471 Desi Prabhandhas
- During the 12th century Saragadheva mentioned in his Sangeetha Ratnakar.
- Prabhandha has 6 angas and 4 dhatus:
5QDifferentiate between kruthi and keerthana.
6Q.write about the life history of Shyama Sastry
- Born 1762-1827
- Parents:Vishvanathayya and Vengalakshmi
- Original name:VenkataSubramnya
- Fondly called ShyamaKrishna
- He was from a Telugu-speaking family
- Mostly composed in Telugu and Sanskrit
- From his compositions, we can come to a conclusion that he liked AnandhaBhairvi and Saaveri
- He popularised the ragam Anandhabhairavi by composing Marivere Gathievvarama in Misrachapu
- His compositions are said to be like Kobbari , a lot of practice in terms of raga, bhava, and Sahitya have to be done to do justice to his compositions
- Karnataka kapi
- He was also well versed with complex thalam and hence called thalaprasthara Syama Sastry
- Mudra:Syama Krishna
- Known for Composing swara Sahitya
- Pachimiriyam Adi Appaya: Guru
- Famous compositions:
- Kamakshi- Bhaiarvai swarajathi-Misrachapu
- Marivere Gathi-AnandhaBhairavi-Misrachapu
- Kamakshi Padayugame-Yadhukula Kambhoji Swarajathi-Misrachapu
- Rave himagiri kumari-thodi-aadhi
- Saroja DhalaNetri-Shankarabharnam-Aadhi thalam
- Shankari shankuru-Saaveri-Trisram
- Subbaraya Sastry (son )
7Q.Explain the life history of Patnam Subramanyam Iyer.
- Ans.Born - 1845-1902
- Father-Bharatham Vaidhyanath Iyer
- From a Tamilian family
- maternal uncle guru
- Guru: Mannambhuchavvadi Venkata Subramanyam Iyer
- Tyagaraja Lineage
- Mostly composed in Telugu and Sanskrith
- Begada sang for 3 days also called Begada Subramanayam Iyer
- Came to Chennai to teach Salem Minakshi Daughters Hence name Patnam ....
- Mudra: Venkatesha
- nadhopasana
- master in rtp,laya,128 aksharas peravartham in simhanandha
- He is also called Junior Thyagaraja as he had his style of composition
- Compositions:
- Neepaadhamulu-Bhairavi
- Marivere Dikkeveru-Lathangi - Khandachapu
- Paridhanamichithe-Bilhari - KhandaCHapu
- Raghu Vamsha - Aadhi- Kadhankuthuhalam
- Anudhinuma
- Thillana pharaju
- Notable shishyas:
- "Tiger Varadhacharyar
- Mysore Vasudheva charya
- Papa and Radha ( Daughters of Salem Minakshi)
8Q.Write the life history of Muthaih Bhagavathar?
- Harikessanallur Muthai Bhagvathar
- 1877-1945
- most import post trinity composer
- Born to Lingam Iyer and Anandham
- He also performed Harikatha hence Bhagavathar
- Composed mostly in Telugu and Sanskrit
- Tyaraja lineage
- Initialy composed in madhyama kala like thyagaraja but later go influenced by Muthu swamy and composed i Vilamba kala
- Mudra- Harikesha
- first principle of swathi Thirunal Academy of music
- Genre : Carnatic Kruthi
- Compositions:
- Amba Vani - Keeravani - Aadhi Thalam
- Arya Devi - Sahana - Aadhi thalam
Ans.
- 1813-1846
- He was born i n royal family of travancore
- Was in power even before he was born and hence called Garbha Sreeman
- He is said to have composed 400 compositions
- Has learnt English,Telugu,Sanskrith,Marathi , Telugu , kanada at a very young age
- He became ruler art age of 16
- encourage both Hindhusthani and Carnatic Though he was of carnatic conssieur
- He encourage alot of court muscians
- Example: Vadivalu
- Thanjavur Brothers
- He composed alot of Varnams and Thillanas
- One of his famous compositions being Bhavayami raghuramam which was said to have initially composed in Saaveri
- But later converted into Raagamalika
- Langauges Composed: Mainly Sanskrith but also used Telugu and Hindi
- Mudra :Padnabha and its variation
- Jalajanabha
- Sarasijanabha
- PankajaNabha
- Saraseeruha Janabha
- Popular compositions
- Deva Deva kalayami-Mayamalavagowla
- Bhogindra shayainam - Kunthalavarali
- Dhanashree Thillana- aadhi Thalam
- BHayami Raghurama-Aadhi thalma - Raagamalika
- Mamava Sadha Janani-Kaanada - aadhi Thalam
10QExplain the Life History of Subbaraya Sastry.
- 1803-1862
- Syama Sastry has two sons
- Subbaraya Sastry and Panju Sastry
- Subbaraya Sastry was the second son
- He got the privilege to study music under the trinity
- Syama Sastry and Tyagaraja were closely related
- So initially he sent him to Tyagaraj
- Mudra Kumara
- Composed in Telugu
- He composed only a dozen of krithis but his raga ras bhava have made them enduring and famous
- Influence of all trinity can be found in his compositions
- Chitta swarams like father
- Madhyama Kalam like Tyagaraja
- Slow paced like Dikshithar
- Compositions:
- Janani - Reethigowla- misrachapu
- Ninnu Vina- Kalyani - Adhi
- Sri Kamalambike-DesyaThodi-Rupaka
11QLife history of Jayadheva.
- poet of 12th century
- Parents Bhoja Deva and radha Devi
- kendhu bhilva
- Born in Orissa
- Devotee of krishna
- JayaDheva was extensively known for his ashtapadhis
- He composed Geetha Govindham
- Deals with divine play of krishna and radha
- He sang it infront of Lord Jaganatha while his wife Padmavathi danced to it
- Sanjeevani Ashtapadhi-reviving his wife from death
- Dharshana Asthapadhi-Lord himself comes and fills in missing parts
- Lord came in the form of jayadheva
- Sringara rasa with Nayaka and nayaki
- Mudra - Sree Jayadheva kavi
- Instrumental in popularising Dashavathara
- Compositions:
- Pasyathi dhishi dhisi- Sindhubhairavi - Aadhi thalam
- Githa Govindham
- Sanjeevana Ashtapadhi
- Shiva Ashtapadhi
12Q Biography of Narayantheertha.
- Ans.Born in 16th century
- Govindha shstrudu
- In guntur disctrict Andhrapradesh
- It is said that he is the incarnation of Jayadheva
- widely known for krishnaleela Tharangini
- deals with krishnas life story starting from Birth to marrying Rukmini
- Life incident of him being caught in a river and then taking sanyasa
- Well versed in music , Natya sastra
- composed in Sanskrit
- write about tharamagams
- Compositions:
- Krishnam Kalaya sakhi
- Jaya Jaya swami- Mukhari - addhi
13QBiography of Annamacharya?
- ans.Sri Tallapaka Annamacharya - 14th century Tallapaka
- from Andhra Pradesh
- Composed mostly in Telugu
- At age of 8, he left tallapaka on command of Venkatesha in his dream
- child prodigy had the vison of alamalumanga
- Mudras like Tiruvenkata,Venkatesha , Venkatadhri
- as he composed extensively on Venkatesha
- widely known as "PadaKavitha Pithamaha"
- His wife Thimmaka who wrote Subhadra kalyanam is considered the first female poet in Telugu literature
- he composed 32000 compositions out which 12000 are available today
- while he was popular in his own days his compositons were later forgotten for 3 centuries, later found engraved on copper plates hidden in room in tirumala
- compositons
- Kancharla Goppana
- 1620-1688th century
- wifes name kamala
- lived in Nelkondapalli,near Bhadrachalam Andhrapradesh
- worked as the Revenue collector under the nizams
- was jailed in Golconda fort
- bhaktha of rama
- He composed Ramadasu Keerthanas
- composed Dasarathi Shathakamu with makutam dasharadhi karunapayonidhi
- It said that he recieved rama taraka manthramu from saint Kabir
- write how he buit the temple in bhadrachalam
- compositions
- ans
- 8th melakartha , 2nd in Netra chakra
- Also called HanumaThodi
- Aarohana: S R G M P D N S
- Aavarohan : S N D P M G R S
- Swarasthans: Shadjamam ,Shudha Rishabaham, Anthara Gandharavam,SudhaMadhyam,Panchamam,Shudha Dhaivatham,Kaisiki Nishadham
- Sampoorna ragam
- This is Murchanakaraka Melam
- Ga,Ma,Dha are raga chaya swaras
- ma and pa are amsa swaras or resting notes
- Panchama Varja Prayogas add beauty to this ragam
- Ri is not nyasa Swaram
- Tristhayi Ragam
- Sarva swara gamaka vareeka rakthi ragam
- It is one of the major ragas
- DnSd RSd, are vishesha prayogas
- Todi seetharammaya sang this ragam for 8 days
- compositions:
- Varnam - Thodi - aadhi thalam-Era napai-Patnam Subramanyam Iyer
- Endhuku Dhayaradha-thodi -Triputa-Thyagaraja
- Kamalambika-Rupaka thalam - Muthu swami dikshithar
- Janya of 22nd Melakartha KharaharaPriya
- Aarohanam:S R2M1 P N2 S
- Aavarohanam: S N2 P M1 R2 S
- Audava Rgaam
- Upanaga Ragam
- Varjya Ragam G D are varjya swarams
- Audava - Audava very suitable for elaboration
- evening ragam
- generally sung at the end of the concert
- Compositions:
- Alakalaladagani-Rupaka-Thyagaraja
- Bhagyadha-Aadhi-Purandhara dasa
- Ashtapadhi-Radhavadhana - Jayadheva - Rupaka
- 21st melakartha
- Aarohan: S R2 G2 M1 P D1N3S
- Aavarohanam: S N3 D1 P M G2 R2 S
- Sampoorna ragam
- Raga chaya swaras r,s,n
- composers begin with r,s,n
- Good scope for aalapana
- its famous janya ragam is kalyana Vasantha
- Popular compositions :
- Ambavani-Muthai Bhagvathar- aadhi
- Varamulona- PatnamSubramanyam iyer- Rupaka
18QKharaharapriya
ans
- 22nd Melakartha
- Aarohana: S R2 G2 M1 P D2 N2 S
- Aavarohana: S N2 D2 P M G2 R2 S
- Sampoorna Ragam
- Murchanakaraka melam
- Elaborate Manodharma can be done
- Sarva swara gamaka vareeka rakthi ragam
- Nyasa swaras and Ragachaya swaras: R G D N
- Amsa swaras: R and P
- Compositions:
- Pakkala Nilabadi-Misrachapu- Tyagaraja
- Samanam Evvaru- Rupaka-Tyagaraja
- Chakkani Raja - Aadhi - Tyagaraj
- HariKhambhoji Janya 28th
- Aarohana:S R2 G3 M1 N2 D2 N2 P D2 N2 S
- Aavarohana:S N2 D2 M1 G3 M1 P G3 R2 S
- Ubhaya Vakra ragam
- Sampoorna ragam
- Gamaka Vareeka Rakthi Ragam
- Thristhayi ragam
- Karuna Rasam
- suitable for singing in the evening
- RagaChaya swaras: R G N
- Compositions:
- Varnam - CHalamela
- Parwathi Kumaram - Rupakam - Muthu swami dikshithair
QAttana
ans. Derived from 29th melakartha DheeraShankarabharnam
- Aarohana: S R2 M1 P N2 S
- Aavarohana:S N3 S D2 P M1 P G2 M1 R2S
- Audava-Samporna ragam
- Varjya ragam in Aarohana
- Upanga ragam
- Gamak Varika ragma
- Rakthi ragam
- Vakra ragam
- Back then it was very famour for operas and harikatha
- Veera rasa
- Raga chaya swaras: G2 M N2 N3
- Compositions:
- Chade Budhi Manura- Tyagaraja-Aadhi
- Bhajana Seyara -Rupaka - Tyagaraja
QNeelambari
ans.
- Shankarabharnam janyam 29th
- Aarohana:S R2 G3 M1 P D2 P N3 S
- Aavarohana: S N3 P M1 G3 R2 G3 S
- Ubhaya Vakra ragam
- Sampoorna ragam
- Eka swara vakra ragam'
- Gamaka vareeka rakthi ragam
- Karuna,bhakthi and vatsyala rasas
- Ragam shines in chowka kala prayogas
- Pa is a resting swara
- Night time is the most appropriate time to sing this ragam
- Compositions:
- Mamamava Madhav-Aadhi -Tharangam- Narayana theerthar
- Uyyala uga vayya-Jhampa Thyagarajaswami
QSadhashiva Brahmahendhra.
- Velinadu couple
- Father somasundhara avadhani mother parwathi
- Named as shiva rama krishna
- As his family deity ramanathaswami
- He took Sanyasam and hence got his name Sahdhashiva
- Sridharachary was his classmate
- ramabhadrabhadra dheekshithar
- He married at 18 but never returned
- Parmasimhendra Saraswathi other spirtual guru
- Navamani mala and guru ratnamalika
- arguable person not easy to convince
- Advaitha vedhantha
- very less compositions are available










Comments
Post a Comment